Essay
Mutations in the intracellular sensor gene NOD2 are associated with Crohn's disease, a chronic severe inflammatory disease of the gastrointestinal tract. NOD2 is normally expressed in Paneth cells of the intestine, as well as in macrophages, monocytes and dendritic cells. To understand the effects of the NOD2 mutation, a line of knock-in mice was generated in which the wild-type NOD2 allele (NOD2+/+) was replaced with a variant disease-associated allele that causes a frameshift mutation in the NOD2 protein coding sequence (NOD2m/m). Isolated macrophages from wild-type mice were and those from NOD2m/m mice were stimulated in vitro with the NOD2 ligand, muramyl dipeptide (MDP, a component of bacterial peptidoglycan), and inflammatory cytokines IL-6 and TNF- were measured 3 hours later, as shown in Figure Q2)24). What is the most likely explanation for why this NOD2 mutation predisposes individuals to Crohn's disease? 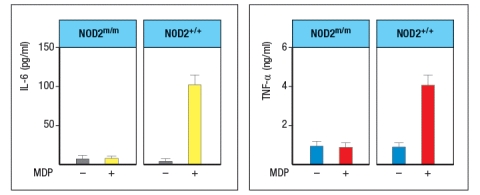
Correct Answer:

Verified
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q1: All autoreactive CD4 T cells are not
Q3: AIRE is a transcriptional regulator that promotes
Q4: T<sub>reg</sub> cells that express FoxP3 are
Q5: A subset of patients with imbalances in
Q6: Immune privileged sites, such as the
Q7: A disease resembling systemic lupus erythematosis (SLE)
Q8: While relatively rare, individuals with a homozygous
Q9: A small subset of patients taking antibiotics
Q10: Nearly 80% of patients with autoimmune
Q11: Based on these data, Fc <span