Essay
Four different clinical isolates of the Gram-positive bacterium, Staphylococcus aureus, are tested for their abilities to resist innate immune defense mechanisms. For these experiments, each bacterial strain is first grown in culture to achieve log-phase replication, and then cultures are supplemented with dilutions of human serum containing normal serum proteins as well as antibodies capable of binding to S. aureus. One hour later, the cultures are analyzed and the numbers of live bacteria are quantitated. The data from this experiment are shown in Figure .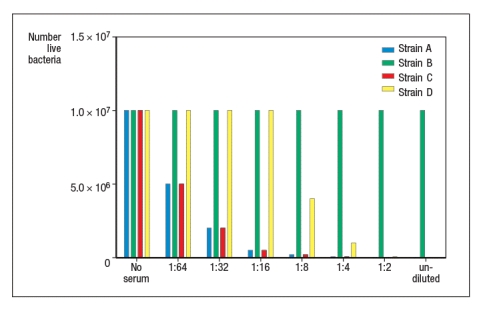
a) From these data, what general conclusions can be reached about the four strains of S. aureus?
To identify the bactericidal mechanisms killing each strain of S. aureus, the serum is depleted of complement C3 by running it over an anti-complement C3 antibody affinity column. The experiment above is then repeated and the data are shown in Figure .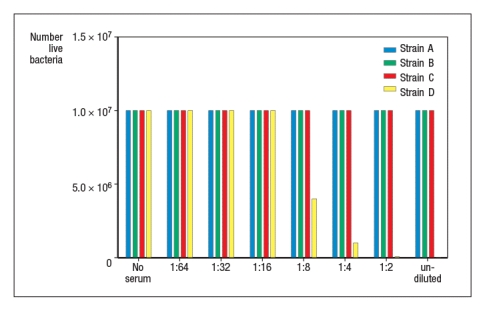
b) What is the most likely mechanism accounting for the killing of strain D in this experiment?
To determine whether strains A and C are susceptible to the same microbicidal pathway, the serum is depleted of antibody by running over an anti-human immunoglobulin affinity column. Following this treatment, it is found that strain A, but not strain C is still killed by incubation with the serum.
c) From these data, what is the most likely mechanism killing S. aureus strain A? What about strain C?
Correct Answer:

Verified
a) Strain A and strain C are equally sen...View Answer
Unlock this answer now
Get Access to more Verified Answers free of charge
Correct Answer:
Verified
View Answer
Unlock this answer now
Get Access to more Verified Answers free of charge
Q22: Our environment contains masses of microorganisms, many
Q23: Multiple pathways for regulating complement activation limit
Q24: One form of anemia results when individuals
Q25: Infants and young children with deficiencies in
Q26: The formation of the C3 convertase is
Q27: Several pathogens produce proteins, either membrane-bound or
Q28: The classical complement pathway is initiated by
Q29: The terminal components of the complement pathway
Q31: The alternative pathway of complement activation has
Q32: Recent studies using mouse models of pulmonary