Essay
Pseudomonas aeruginosa is a Gram-negative bacterium that causes severe, and often life-threatening infections in immunocompromised individuals. In susceptible individuals, P. aeruginosa can establish infections in a wide range of tissues, including the lung, the GI tract, the eye, the ear, the urinary tract, the skin, and the blood. This bacterium is common in the environment, and is found on the skin of approximately 5% of healthy individuals. It is often found on hospital equipment, such as ventilators and catheters, and as a consequence, P. aeruginosa accounts for ~10% of hospital-acquired infections. To study the role of complement in the early innate immune response to P. aeruginosa, the following studies in mice were performed. Mice deficient in complement C3 or C5 (C3-/- or C5-/-, respectively) were infected by intratracheal inoculation with 105 colony forming units (CFU) of P. aeruginosa, and survival was monitored over the first 72 hrs post-infection. The data from these studies are shown in Figure . Genetic data from human population studies also indicate that Individuals with genetic deficiencies in one of the collectins or ficolins show increased susceptibility to P. aeruginosa infections. 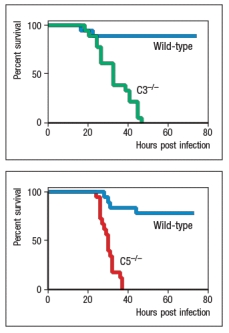
a) Based on these data, evaluate the importance of complement in protection against P. aeruginosa infection, and describe the most likely complement pathway(s) involved in pathogen recognition and in pathogen destruction.
Another group of individuals that are highly susceptible to P. aeruginosa infections are patients with the disease cystic fibrosis. These individuals suffer from the production of a thick mucus secretion in their lungs, which clogs the bronchial tubes. A similar increase in viscosity of bodily secretions is seen in these patients' sweat, digestive fluid, and gastrointestinal mucus. In these patients, the most common form of lung infection is that of P. aeruginosa.
b) What is the most likely explanation for the increased susceptibility of cystic fibrosis patients to P. aeruginosa and other infections?
Correct Answer:

Verified
a) Complement is essential for early pro...View Answer
Unlock this answer now
Get Access to more Verified Answers free of charge
Correct Answer:
Verified
View Answer
Unlock this answer now
Get Access to more Verified Answers free of charge
Q16: Even when the complement cascade fails to
Q17: The classical and lectin pathways of complement
Q18: Women with urinary tract infections caused by<br>A)
Q19: Pathogenic infections induce damage to the host
Q20: Patients with recurrent infections of Neisseria meningitidis,
Q22: Our environment contains masses of microorganisms, many
Q23: Multiple pathways for regulating complement activation limit
Q24: One form of anemia results when individuals
Q25: Infants and young children with deficiencies in
Q26: The formation of the C3 convertase is