Multiple Choice
Physicians routinely give their patients pulmonary function tests in order to measure characteristics of lung function. The most common of these tests, spirometry, measures both the volume and the speed of air entering and exiting the lungs. In this test, a person first breathes normally while breathing into a spirometer, a machine that measures air volume and air speed. Then the person takes the deepest breath possible and exhales as hard as possible for 6 seconds into the spirometer. The resulting data are plotted on a graph of volume (y axis) versus time (x axis) . Spirometry is useful not only for assessing lung function in healthy patients but also for characterizing patients with lung conditions such as pulmonary fibrosis, asthma, or emphysema.
A sample graph for a healthy adult male is shown below. Normal breathing occurs between points A and B, a maximal inhalation occurs at point C, and a maximal exhalation occurs at point D. Normal breathing resumes between points E and F.
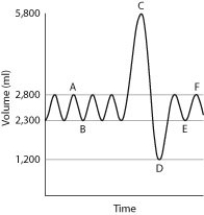
-For this data set, how much air is exhaled during a normal breath?
A) 500 mL
B) 1,200 mL
C) 2,300 mL
D) 2,800 mL
Correct Answer:

Verified
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q2: What part of the respiratory system does
Q3: Oxygen moves from blood into the interstitial
Q4: Inhalation in humans is achieved by<br>A) contraction
Q5: Air leaving human lungs during exhalation contains<br>A)
Q6: Which of the following animals would most
Q8: Compared to the vital capacity, how much
Q9: Medullary breathing centers directly sense and respond
Q10: Many amphibians (including many frogs, toads,
Q11: One advantage of gas exchange in water
Q12: The tracheal system of an insect is