Multiple Choice
The next few questions refer to the following description and Table 25.1.
Diatoms are encased in Petri-platelike cases (valves) made of translucent hydrated silica whose thickness can be varied. The material used to store excess calories can also be varied. At certain times, diatoms store excess calories in the form of the liquid polysaccharide, laminarin, and at other times as oil. Table 25.1 shows data concerning the density (specific gravity) of various components of diatoms, and of their environment.
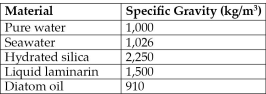 Table 25.1 Specific Gravities of Materials Relevant to Diatoms
Table 25.1 Specific Gravities of Materials Relevant to Diatoms
-Water's density and, consequently, its buoyancy decrease at warmer temperatures. Based on this consideration and using data from Table 25.1, at which time of year should one expect diatoms to be storing excess calories mostly as oil?
A) mid-winter
B) early spring
C) late summer
D) late fall
Correct Answer:

Verified
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q1: According to the endosymbiotic theory of the
Q2: An individual mixotroph loses its plastids, yet
Q34: Giardia lamblia is an intestinal parasite of
Q45: Living diatoms contain brownish plastids. If global
Q45: You are given five test tubes, each
Q54: Plastids that are surrounded by more than
Q61: If true, which of the following is
Q62: Which of the following was derived from
Q66: The oldest fossil eukaryote that can be
Q75: You are given the task of designing