Multiple Choice
Groundwater often has low levels of dissolved oxygen because it is not continually exposed to the atmosphere. When groundwater reaches the surface, the following reaction involving soluble iron(II) can occur. What are the oxidation numbers of the elements in the product, Fe(OH) 3? 4Fe2+(aq) 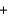 O2(g)
O2(g) 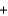 2H2O(l )
2H2O(l ) 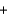 8OH-
8OH- 4Fe(OH) 3(s)
4Fe(OH) 3(s)
A) Fe 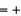 2, O = -2, H = 0
2, O = -2, H = 0
B) Fe 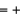 2, O = -1, H = -1
2, O = -1, H = -1
C) Fe 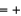 4, O = -2, H = +1
4, O = -2, H = +1
D) Fe 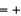 3, O
3, O  1, H
1, H 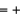 1
1
E) Fe 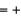 3, O
3, O  2, H
2, H 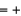 1
1
Correct Answer:

Verified
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q16: Write the net ionic equation for the
Q17: Which one of the following statements is
Q18: In the dilution of 10.0 mL of
Q19: A typical adult body contains about 6.0
Q20: Mercury is one of the most
Q22: Which of the following ionic compounds is
Q23: What is the molar concentration of sodium
Q24: In a demonstration of strong electrolytes, weak
Q25: Hartmann's solution is used in intravenous therapy
Q26: When the oxidation reduction reaction shown here