Multiple Choice
An electrical power supply, such as a battery, generates an electrical potential (voltage, V) which varies depending on how much current (i) it is delivering. The integral 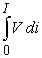 represents the total power (energy per unit time) being given off by the battery when it is producing a current I. The useful electrical power, however, is just the product
represents the total power (energy per unit time) being given off by the battery when it is producing a current I. The useful electrical power, however, is just the product 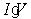 . The difference between the total and the electrical power represents power that is wasted (and that accumulates as heat) . Consider a hypothetical battery with a voltage vs. current curve described by the equation
. The difference between the total and the electrical power represents power that is wasted (and that accumulates as heat) . Consider a hypothetical battery with a voltage vs. current curve described by the equation 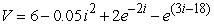 . If the battery is producing a current of 4 amperes, how much electrical power is being produced, and how much power is being wasted?
. If the battery is producing a current of 4 amperes, how much electrical power is being produced, and how much power is being wasted?
A) 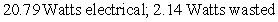
B) 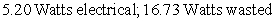
C) 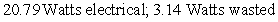
D) 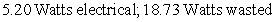
Correct Answer:

Verified
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q42: The pdf describing the chance that a
Q43: A force of 6 pounds stretches a
Q44: The base of a solid V is
Q45: The thrust on a particular missile is
Q46: Identify the initial conditions y(0) and y'(0)
Q48: Find the mean of the random variable
Q49: Identify the mass of a thin wire
Q50: Find the volume of the solid formed
Q51: Identify the region (solid lines) and axis
Q52: Find a value of c for which