Multiple Choice
Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infects cells that have both CD4 and CCR5 cell surface molecules. The viral nucleic acid molecules are enclosed in a protein capsid, and the protein capsid is itself contained inside an envelope consisting of a lipid bilayer membrane and viral glycoproteins. One hypothesis for viral entry into cells is that binding of HIV membrane glycoproteins to CD4 and CCR5 initiates fusion of the HIV membrane with the plasma membrane, releasing the viral capsid into the cytoplasm. An alternative hypothesis is that HIV gains entry into the cell via receptor-mediated endocytosis, and membrane fusion occurs in the endocytotic vesicle. To test these alternative hypotheses for HIV entry, researchers labelled the lipids on the HIV membrane with a red fluorescent dye. 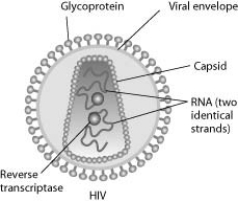
-In an HIV-infected cell producing HIV virus particles, the viral glycoprotein is expressed on the plasma membrane. How do the viral glycoproteins get to the plasma membrane? They are synthesised ________.
A) on ribosomes on the plasma membrane
B) by ribosomes in the rough ER and arrive at the plasma membrane in the membrane of secretory vesicles
C) on free cytoplasmic ribosomes and then inserted into the plasma membrane
D) by ribosomes in the rough ER, secreted from the cell, and inserted into the plasma membrane from the outside
Correct Answer:

Verified
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q17: Several epidemic microbial diseases of earlier centuries
Q18: Familial hypercholesterolemia is characterised by _.<br>A) defective
Q20: A research team is working on the
Q21: Five dialysis bags, constructed of a type
Q22: The solutions in the two arms of
Q28: Which of the following types of molecules
Q41: What will happen to a red blood
Q52: An organism with a cell wall would
Q59: The voltage across a membrane is called
Q64: A phospholipid bilayer with equal amounts of