Multiple Choice
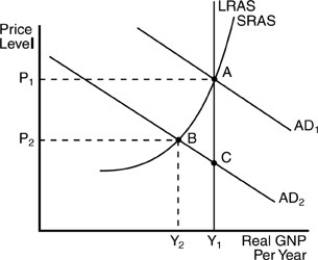
-In the above figure, start with the economy in equilibrium at point A. Then an unanticipated reduction in aggregate demand triggers a shift from AD1 to AD2. In the short run, this would cause
A) the price level to fall from P1 to P2, real Gross Domestic Product (GDP) to fall from Y1 to Y2, and the rate of unemployment to increase.
B) the price level to move from P1 to P2, but real Gross Domestic Product (GDP) would stay at Y1.
C) the price level to fall by some amount less than P1 but greater than P2, and the rate of unemployment would decrease.
D) no change in either the price level or real Gross Domestic Product (GDP) , but a decrease in unemployment.
Correct Answer:

Verified
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q139: Suppose the economy is in equilibrium when
Q140: The rational expectations hypothesis is based on
Q141: If the Fed engages in open market
Q142: According to the real-business-cycle perspective<br>A) the economy
Q143: Costs that tend to deter firms from
Q145: If the rate of growth in the
Q146: What did Milton Friedman and E.S. Phelps
Q147: People might experience rational inattention if they<br>A)
Q148: The stagflation experienced in the U.S. during
Q149: The proposition that policy actions have no