Multiple Choice
Use the following to answer questions
Scenario I
Scenario I is based on fabricated data inspired by the following study:
Curry, N. A. & Kasser, T. (2005) . Can coloring mandalas reduce anxiety? Art Therapy: Journal of American Art Therapy Association, 22(2) 81-85.
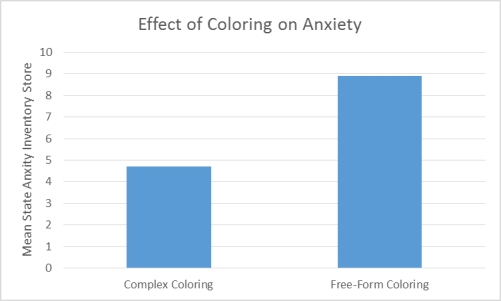
Effect of Coloring on Anxiety
Curry and Kasser were interested in examining whether coloring complex geometric patterns reduces anxiety. To that end, they induced anxiety in 84 undergraduate volunteers from their university. Following anxiety induction the participants were divided into two coloring conditions. To determine which condition each participant would be in the researchers put all of their names in a hat. The first name drawn was placed in group 1, the second name drawn was placed in group 2, the third name drawn was placed in group 1, and so on. Those in the complex geometric coloring condition (group 1) were given a paper with a plaid pattern or the outline of a mandala. Those in the control condition (group 2) were given a blank piece of paper. After 20 minutes of coloring all of the participants completed a self-administered State Anxiety Inventory (SAI) . Lower SAI scores indicate low levels of anxiety whereas higher SAI scores indicate high levels of anxiety. The mean SAI scores of each coloring condition were compared to determine whether the type of coloring one does affects anxiety. The results revealed that those who colored a complex geometric pattern had significantly different levels of anxiety than those who colored on a blank sheet of paper. Curry and Kasser concluded that coloring causes a change in anxiety, but only when coloring requires a certain amount of attention and focus.
Figure 1. Effect of Coloring on Anxiety
-(Scenario I) Had participants in this study been allowed to select whether they wanted to color the mandala, the plaid pattern, or the blank paper, the researchers would have used __________ assignment.
A) random
B) nonrandom
C) quasi-random
D) matched-pair
Correct Answer:

Verified
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q1: When entering data into a statistical computer
Q69: In a study examining the impact of
Q70: Unlike a correlation, the two-group experimental design
Q100: Isabel would like for her experiment to
Q133: Research has shown that bad weather puts
Q134: In presenting the findings of an independent
Q135: An important condition for establishing causation is
Q137: After conducting an independent samples t-test on
Q139: Experimenters use random assignment of participants to
Q142: The _ hypothesis is a clear and