Multiple Choice
Imagine we wanted to investigate whether the reason for quitting smoking affects success rate. We recruited a sample of 120 smokers. Half wanted to quit to improve their appearance (yellow teeth and bad breath, etc.) , and half wanted to quit to improve their health (life expectancy, etc.) . After six months we measured how successful they had been at quitting smoking. The data were skewed, so we ran a Mann-Whitney test on the data (output below) . Which of the following sentences correctly reports the results from the Mann-Whitney test?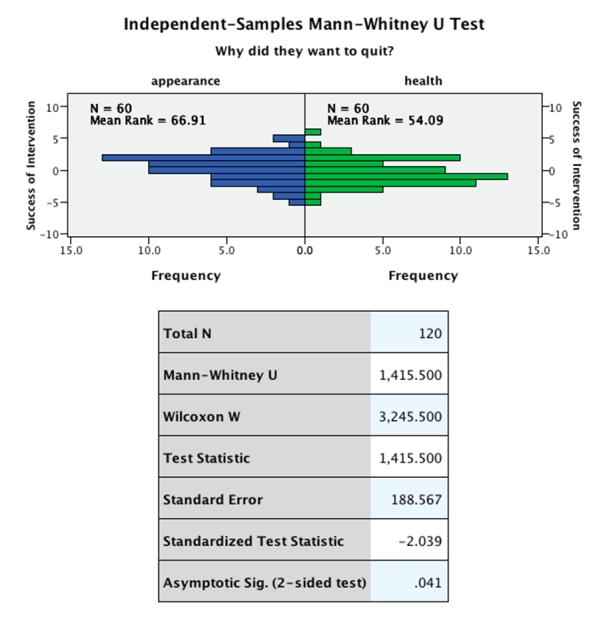
A) People who wanted to quit smoking to improve their appearance did not significantly differ from those who wanted to quit to improve their health, U = 1415.50, z = −2.04, p = .04.
B) People who wanted to quit smoking to improve their appearance (M = 66.91) were significantly more successful at quitting than those who wanted to quit to improve their health (M = 54.09) , U = −2.04, z = 188.57, p = .04.
C) People who wanted to quit smoking to improve their appearance were significantly more successful at quitting than those who wanted to quit to improve their health, U = 1415.50, z = −2.04, p = .04.
D) People who wanted to quit smoking to improve their health were significantly more successful at quitting than those who wanted to quit to improve their appearance, U = 1415.50, z = −2.04, p = .04.
Correct Answer:

Verified
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q7: What is the non-parametric equivalent of the
Q8: When the groups have equal numbers of
Q9: What is the problem with doing multiple
Q10: Non-parametric tests are used when:<br>A)The assumptions of
Q11: You have carried out a Kruskal-Wallis test.
Q13: A researcher measured people's physiological reactions to
Q14: Which of the following non-parametric tests does
Q15: What can be done to reduce the
Q16: A researcher measured people's physiological reactions while
Q17: When the groups have unequal numbers of