Multiple Choice
Calculate ΔG° for 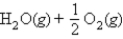

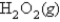
At 600. K, using the following data:
H2(g) + O2(g)  H2O2 Kp = 2.3 × 106 at 600.
H2O2 Kp = 2.3 × 106 at 600.
K2H2(g) + O2(g)  2H2O(g) Kp = 1.8 × 1037 at 600. K
2H2O(g) Kp = 1.8 × 1037 at 600. K
A) -220 kJ
B) -350 kJ
C) +140 kJ
D) -290 kJ
E) +290 kJ
Correct Answer:

Verified
Correct Answer:
Verified
Related Questions
Q27: In an isothermal process, the pressure on
Q28: A sample contains 12.0 moles of a
Q29: At 1 atm, a liquid is heated
Q30: Assuming ΔH° and ΔS° are temperature independent,
Q31: The process H<sub>2</sub>O(g) → H<sub>2</sub>O(l) takes place
Q33: If the change in entropy of the
Q34: For the vaporization of a liquid at
Q35: The reaction is allowed to proceed until
Q36: Identify the second law of thermodynamics.<br>A) In
Q37: Consider the dissociation reaction of the acid