Multiple Choice
Ibuprofen is a weak acid with a pKa of 4.9 (shown with the ionizable hydrogen with a star) . It is absorbed through the stomach and the small intestine as a function of polarity-charged and very polar molecules are absorbed slowly; neutral hydrophobic molecules absorb quickly. If the stomach pH is about 1.5 and the small intestine pH is about 6, where (and why) will more ibuprofen be absorbed into the bloodstream? 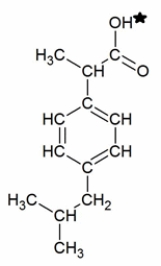
A) More ibuprofen will be absorbed in the small intestine because it will be uncharged due to the pH being greater than the pKa.
B) More ibuprofen will be absorbed in the stomach because it will be uncharged due to the pH being lower than the pKa.
C) More ibuprofen will be absorbed in the small intestine because it will be charged due to the pH being greater than the pKa.
D) More ibuprofen will be absorbed in the stomach because it will be charged due to the pH being lower than the pKa.
E) Ibuprofen will be absorbed equally well in both the stomach and small intestine.
Correct Answer:

Verified
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q10: Which statement does NOT describe a strategy
Q11: Explain the fact that triethylammonium chloride ((CH<sub>3</sub>CH<sub>2</sub>)<sub>3</sub>N-HCl)
Q12: The conjugate base of H<sub>2</sub>PO<sub>4</sub><sup> </sup><sup>-</sup><sup>1</sup> is:<br>A)
Q13: For each of the pairs below, circle
Q14: Which diagram CORRECTLY represent a hydrogen bond?
Q16: Which statement about biologically important gases is
Q17: Which result influences the lower limit for
Q18: A compound has a pK<sub>a</sub> of 7.4.
Q19: Which attribute contributes to water's unusual properties?<br>A)
Q20: The OH<sup>-</sup> concentration of a solution is