Essay
(Requires Appendix)(Continuation from Chapter 4)At a recent county fair,you observed that at one stand people's weight was forecasted,and were surprised by the accuracy (within a range).Thinking about how the person could have predicted your weight fairly accurately (despite the fact that she did not know about your "heavy bones"),you think about how this could have been accomplished.You remember that medical charts for children contain 5%,25%,50%,75% and 95% lines for a weight/height relationship and decide to conduct an experiment with 110 of your peers.You collect the data and calculate the following sums: 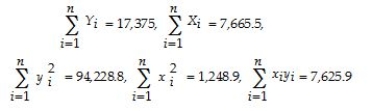 where the height is measured in inches and weight in pounds.(Small letters refer to deviations from means as in zi = Zi -
where the height is measured in inches and weight in pounds.(Small letters refer to deviations from means as in zi = Zi - 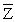 . )
. )
(a)Calculate the homoskedasticity-only standard errors and,using the resulting t-statistic,perform a test on the null hypothesis that there is no relationship between height and weight in the population of college students.
(b)What is the alternative hypothesis in the above test,and what level of significance did you choose?
(c)Statistics and econometrics textbooks often ask you to calculate critical values based on some level of significance,say 1%,5%,or 10%.What sort of criteria do you think should play a role in determining which level of significance to choose?
(d)What do you think the relationship is between testing for the significance of the slope and whether or not the regression R2 is zero?
Correct Answer:

Verified
(a)The formula for the homoskedasticity-...View Answer
Unlock this answer now
Get Access to more Verified Answers free of charge
Correct Answer:
Verified
View Answer
Unlock this answer now
Get Access to more Verified Answers free of charge
Q4: With heteroskedastic errors, the weighted least squares
Q13: Explain carefully the relationship between a confidence
Q24: Your textbook discussed the regression model when
Q27: In many of the cases discussed in
Q28: Using 143 observations,assume that you had estimated
Q28: The homoskedastic normal regression assumptions are all
Q31: The only difference between a one- and
Q32: Consider the following two models involving binary
Q34: If the absolute value of your calculated
Q34: Under the least squares assumptions (zero conditional