Essay
(Continuation of the Purchasing Power Parity question from Chapter 4)The news-magazine The Economist regularly publishes data on the so called Big Mac index and exchange rates between countries.The data for 30 countries from the April 29,2000 issue is listed below:
Price of Actual Exchange Rate
Country Currency Big Mac per U.S.dollar
Indonesia Rupiah 14,500 7,945
Italy Lira 4,500 2,088
South Korea Won 3,000 1,108
Chile Peso 1,260 514
Spain Peseta 375 179
Hungary Forint 339 279
Japan Yen 294 106
Taiwan Dollar 70 30.6
Thailand Baht 55 38.0
Czech Rep.Crown 54.37 39.1
Russia Ruble 39.50 28.5
Denmark Crown 24.75 8.04
Sweden Crown 24.0 8.84
Mexico Peso 20.9 9.41
France Franc 18.5 7.07
Israel Shekel 14.5 4.05
China Yuan 9.90 8.28
South Africa Rand 9.0 6.72
Switzerland Franc 5.90 1.70
Poland Zloty 5.50 4.30
Germany Mark 4.99 2.11
Malaysia Dollar 4.52 3.80
New Zealand Dollar 3.40 2.01
Singapore Dollar 3.20 1.70
Brazil Real 2.95 1.79
Canada Dollar 2.85 1.47
Australia Dollar 2.59 1.68
Argentina Peso 2.50 1.00
Britain Pound 1.90 0.63
United States Dollar 2.51
The concept of purchasing power parity or PPP ("the idea that similar foreign and domestic goods … should have the same price in terms of the same currency," Abel,A.and B.Bernanke,Macroeconomics,4th edition,Boston: Addison Wesley,476)suggests that the ratio of the Big Mac priced in the local currency to the U.S.dollar price should equal the exchange rate between the two countries.
After entering the data into your spread sheet program,you calculate the predicted exchange rate per U.S.dollar by dividing the price of a Big Mac in local currency by the U.S.price of a Big Mac ($2.51).To test for PPP,you regress the actual exchange rate on the predicted exchange rate.
The estimated regression is as follows: 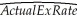 = -27.05 + 1.35 × 1.35×Pr edExRate R2 = 0.994,n = 29,SER = 122.15
= -27.05 + 1.35 × 1.35×Pr edExRate R2 = 0.994,n = 29,SER = 122.15
(23.74)(0.02)
(a)Your spreadsheet program does not allow you to calculate heteroskedasticity robust standard errors.Instead,the numbers in parenthesis are homoskedasticity only standard errors.State the two null hypothesis under which PPP holds.Should you use a one-tailed or two-tailed alternative hypothesis?
(b)Calculate the two t-statistics.
(c)Using a 5% significance level,what is your decision regarding the null hypothesis given the two t-statistics? What critical values did you use? Are you concerned with the fact that you are testing the two hypothesis sequentially when they are supposed to hold simultaneously?
(d)What assumptions had to be made for you to use Student's t-distribution?
Correct Answer:

Verified
(a)Under PPP,H0 : β0 = 0 and Ho : β1 = 1...View Answer
Unlock this answer now
Get Access to more Verified Answers free of charge
Correct Answer:
Verified
View Answer
Unlock this answer now
Get Access to more Verified Answers free of charge
Q3: The homoskedasticity-only estimator of the variance of
Q4: You have collected data for the 50
Q5: The p-value for a one-sided left-tail test
Q6: Your textbook discussed the regression model when
Q7: Using the textbook example of 420 California
Q9: The neoclassical growth model predicts that for
Q11: (continuation from Chapter 4,number 3)You have obtained
Q13: The error term is homoskedastic if<br>A)var(ui <img
Q55: The t-statistic is calculated by dividing<br>A)the OLS
Q58: The effect of decreasing the student-teacher ratio