Essay
Let 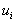 be distributed N(0,
be distributed N(0, 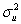 ),i.e. ,the errors are distributed normally with a constant variance (homoskedasticity).This results in
),i.e. ,the errors are distributed normally with a constant variance (homoskedasticity).This results in 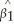 being distributed N(β1,
being distributed N(β1, 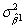 ),where
),where 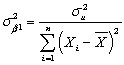 .Statistical inference would be straightforward if
.Statistical inference would be straightforward if 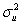 was known.One way to deal with this problem is to replace
was known.One way to deal with this problem is to replace 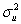 with an estimator
with an estimator 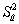 .Clearly since this introduces more uncertainty,you cannot expect
.Clearly since this introduces more uncertainty,you cannot expect 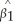 to be still normally distributed.Indeed,the t-statistic now follows Student's t distribution.Look at the table for the Student t-distribution and focus on the 5% two-sided significance level.List the critical values for 10 degrees of freedom,30 degrees of freedom,60 degrees of freedom,and finally ∞ degrees of freedom.Describe how the notion of uncertainty about
to be still normally distributed.Indeed,the t-statistic now follows Student's t distribution.Look at the table for the Student t-distribution and focus on the 5% two-sided significance level.List the critical values for 10 degrees of freedom,30 degrees of freedom,60 degrees of freedom,and finally ∞ degrees of freedom.Describe how the notion of uncertainty about 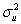 can be incorporated about the tails of the t-distribution as the degrees of freedom increase.
can be incorporated about the tails of the t-distribution as the degrees of freedom increase.
Correct Answer:

Verified
More uncertainty implies that the tales ...View Answer
Unlock this answer now
Get Access to more Verified Answers free of charge
Correct Answer:
Verified
View Answer
Unlock this answer now
Get Access to more Verified Answers free of charge
Q9: In the presence of heteroskedasticity, and assuming
Q18: The construction of the t-statistic for a
Q45: Heteroskedasticity means that<br>A)homogeneity cannot be assumed automatically
Q48: Imagine that you were told that the
Q49: (Requires Appendix material and Calculus)Equation (5.36)in your
Q50: In general,the t-statistic has the following form:<br>A)
Q52: The proof that OLS is BLUE requires
Q56: Using the California School data set from
Q57: You have collected 14,925 observations from the
Q58: One of the following steps is not