Essay
Define the GLS estimator and discuss its properties when Ω is known.Why is this estimator sometimes called infeasible GLS? What happens when Ω is unknown? What would the Ω matrix look like for the case of independent sampling with heteroskedastic errors,where var(ui  Xi)= ch(Xi)= σ2
Xi)= ch(Xi)= σ2 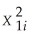 ? Since the inverse of the error variance-covariance matrix is needed to compute the GLS estimator,find Ω-1.The textbook shows that the original model Y = Xβ + U will be transformed into
? Since the inverse of the error variance-covariance matrix is needed to compute the GLS estimator,find Ω-1.The textbook shows that the original model Y = Xβ + U will be transformed into 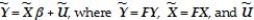 = FU,and
= FU,and 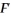 F = Ω-1.Find F in the above case,and describe what effect the transformation has on the original data.
F = Ω-1.Find F in the above case,and describe what effect the transformation has on the original data.
Correct Answer:

Verified
 GLS= (
GLS= (  Ω-1X)-1(
Ω-1X)-1(  Ω-1Y).The key point f...
Ω-1Y).The key point f...View Answer
Unlock this answer now
Get Access to more Verified Answers free of charge
Correct Answer:
Verified
View Answer
Unlock this answer now
Get Access to more Verified Answers free of charge
Q21: The homoskedasticity-only F-statistic is<br>A) <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB2833/.jpg" alt="The
Q23: You have obtained data on test scores
Q24: The extended least squares assumptions in the
Q27: Your textbook derives the OLS estimator as
Q28: An estimator of β is said to
Q29: The OLS estimator for the multiple regression
Q30: Let Y = <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB2833/.jpg" alt="Let Y
Q32: The OLS estimator<br>A)has the multivariate normal asymptotic
Q36: The assumption that X has full column
Q42: The presence of correlated error terms creates