Multiple Choice
Future Plastics manufactures plastic products for industrial use worldwide. In order to meet demand, they are considering setting up a facility in each region in order to lower transportation cost and to possibly avoid duties that could be imposed if the product is imported from another region. The disadvantage of this approach is that plants are sized to meet local demand and may not fully exploit economies of scale. Therefore, Future Plastics is also interested in determining the appropriate size of the facility to build in each location and are choosing between facilities with capacities of 5 or 10 million.
The fixed costs of each facility as well as the cost of shipping between regions is shown in the table below. The decision variables are defined as follows:
Xij = quantity shipped from supply region i to demand region j. i = 1, 2, 3, 4 and j = 1, 2, 3, 4.
Yik = 1 if facility k is selected for supply region i; 0 otherwise, where i = 1, 2, 3, 4 for each supply region; k = 1 (low capacity facility) or 2 (high capacity facility)
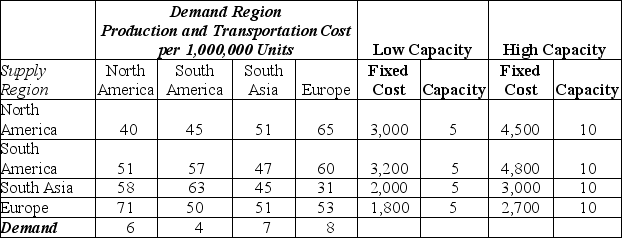
-The constraint for the North American supply region is:
A) X11 + X21 + X31 + X34 - 5Y11 - 10Y21 ≤ 0
B) X11 + X12 + X13 + X14 - 5Y11 - 10Y12 ≤ 0
C) X11 + X12 + X13 + X14 - 3200Y11 - 4800Y12 ≤ 0
D) X11 + X12 + X13 + X14 - 5Y11 - 10Y12 = 0
Correct Answer:

Verified
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q46: Types of integer programming models are _.<br>A)
Q47: Due to increased sales, a company
Q48: A rounded-down integer solution can result in
Q49: In a capital budgeting problem, if either
Q50: Saba conducts regular tours of his favorite
Q52: The Wiethoff Company has a contract
Q53: The production planner for Airbus showed his
Q54: Consider a capital budgeting example with five
Q55: Rounding non-integer solution values up to the
Q56: If we are solving a 0-1 integer