True/False
For a continuous random variable x and constant a, P(x 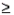 a) = P(x >a) and P(x
a) = P(x >a) and P(x 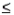 a) = P(x < a).
a) = P(x < a).
Correct Answer:

Verified
Correct Answer:
Verified
Related Questions
Q8: A random variable X is normally distributed
Q18: The mean, median, and standard deviation of
Q101: Examples of continuous probability distributions include the
Q128: Using the standard normal curve, the area
Q196: Assume that x is normally distributed random
Q198: If a normal curve appears more peaked,
Q199: Given that Z is a standard normal
Q200: Braking Distance Narrative<br>For a car travelling 60
Q202: Let <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4962/.jpg" alt="Let be
Q205: Suppose that the probability p of success