Essay
Population Samples Narrative
A sample is selected from one of two populations, 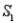 and
and 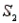 , with probabilities P(
, with probabilities P( 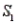 ) = 0.80 and P(
) = 0.80 and P( 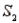 ) = 0.20. If the sample has been selected from
) = 0.20. If the sample has been selected from 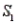 , the probability of observing an event A is P(A/
, the probability of observing an event A is P(A/ 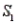 ) = 0.15. Similarly, If the sample has been selected from
) = 0.15. Similarly, If the sample has been selected from 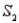 , the probability of observing A is P(A/
, the probability of observing A is P(A/ 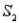 ) = 0.25.
) = 0.25.
-Refer to Population Samples Narrative. If a sample is randomly selected and event A is observed, what is the probability that the sample was selected from population 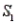 ? From population
? From population 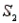 ?
?
Correct Answer:

Verified
Using the result results of pa...View Answer
Unlock this answer now
Get Access to more Verified Answers free of charge
Correct Answer:
Verified
View Answer
Unlock this answer now
Get Access to more Verified Answers free of charge
Q104: Late Night Talk Shows Narrative<br>Let A be
Q105: Salary of Working Mothers Narrative<br>A researcher studied
Q106: Psychological Tests Narrative<br>A psychologist tests Grade 7
Q107: Defective Bolts Narrative<br>Approximately 5% of the bolts
Q108: Casino Card Game Narrative<br>The probability distribution of
Q110: Waste Management Project Narrative<br>A federal agency is
Q111: Number of Cars Narrative<br>Let the random variable
Q112: Late Night Talk Shows Narrative<br>Let A be
Q113: Coffee Brands Narrative<br>A food company plans to
Q114: A graduate student has decided she needs