Multiple Choice
Corporate policy at Weber Pty Ltd requires that all transfers between divisions be recorded at variable cost as a transfer price. Divisional managers have complete autonomy in choosing their sources of customers and suppliers. The Milling Division sells a product called RK2. Forty per cent of the sales of RK2 are to the Products Division, while the remainder of the sales are to outside customers. The manager of the Milling Division is evaluating a special offer from an outside customer for 10 000 units of RK2 at a per unit price of $15. If the special offer were accepted, the Milling Division would be unable to supply those units to the Products Division. The Products Division could purchase those units from another supplier for $17 per unit. Annual capacity for the Milling Division is 25 000 units. The 2014 budget information for the Milling Division, based on full capacity, is presented below. 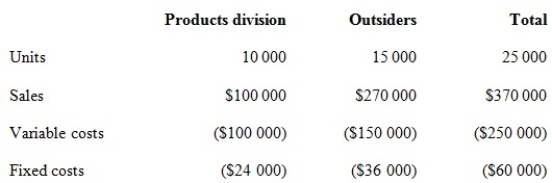
Assume that demand increases for the Milling Division. 20 000 units can be sold at the regular price to outside customers and the Products Division's annual demand remains at 10 000 units. What is the transfer price that would be calculated under the general transfer-pricing formula?
A) $12.00
B) $14.00
C) $16.00
D) $18.00
Correct Answer:

Verified
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q92: Transfer prices should not be based on
Q93: Which of the following statements unambiguously describes
Q94: If a manager were responsible for a
Q95: Hamilton has excess capacity. If the company
Q96: Fruities Ltd has two divisions, Durian Division
Q97: An example of a profit centre is
Q98: Corporate policy at Weber Pty Ltd requires
Q99: Which of the following information should be
Q101: Companies believe that when performance measures are
Q102: Which of the following statements about business