Essay
One way that nociception (the sensation of pain) is modulated is by presynaptic inhibition of transmitter release from the nociceptive sensory neuron onto its postsynaptic target that takes information to the central nervous system (Figure Q3-48). Endogenous opioids (endorphins) are released onto the presynaptic terminal of the nociceptive sensory neuron. 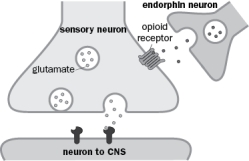 Figure Q3-48
Figure Q3-48
A. If endorphins eventually result in an increased probability of Ca2+ channel closure, what will happen to the amount of glutamate release from the sensory neuron? Increase or decrease?
B. What would happen to Ca2+ channels if a G protein were activated in the absence of endorphin release?
C. Would endorphin result in synaptic facilitation or depression?
Correct Answer:

Verified
It will decrease. Ca2+ is necessary to evo...View Answer
Unlock this answer now
Get Access to more Verified Answers free of charge
Correct Answer:
Verified
View Answer
Unlock this answer now
Get Access to more Verified Answers free of charge
Q40: If you stimulate a glutamatergic presynaptic neuron
Q41: A series of critical experiments showed the
Q42: Myasthenia gravis is an autoimmune neuromuscular disease
Q43: Which molecules activate the ionotropic AChR? Choose
Q44: The presynaptic active zone must line-up with
Q46: In Figure Q3-52, a 5-ms depolarizing current
Q47: Syt1 point mutation is a point mutation
Q48: What are the three main SNARE proteins?<br>A)
Q49: Flies with the Shibire mutant become paralyzed
Q50: What is a reversal potential (E<sub>rev</sub>)?