Multiple Choice
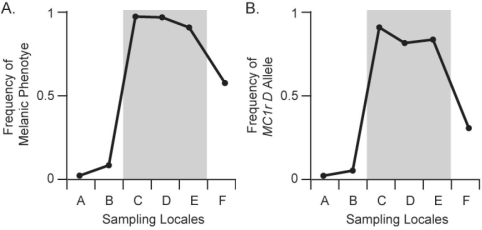
Figure 22.2
The distribution of pocket- mouse coat colours in several Arizona populations is associated with substrate colour Some populations live on light- coloured granite substrate, and others live on dark volcanic rock. In Figure 22.2, chart A shows the frequency of the melanic dark) coat phenotype across six populations. Populations C, D, and E live on dark volcanic rock; populations A, B, and F live on light- coloured granite. Chart B shows the
Frequency of the Melanocortin- 1 receptor Mc1r) allele across these populations. The Mc1r alleles, D and d, differ by four amino acids; mice with DD and Dd genotypes have dark coats, whereas mice with dd genotype are light coloured. Which of the following statements best interprets the results shown in charts A and B?
A) Frequency of the D allele is closely associated with both the melanic phenotype and the presence of dark substrate colour.
B) Frequency of the D allele is closely associated with the melanic phenotype, but is unrelated to the presence of dark substrate colour.
C) Frequency of the D allele is not associated with the melanic phenotype, but is associated with the presence of dark substrate colour.
D) Frequency of the D allele is associated neither with the melanic phenotype nor with the presence of dark substrate colour.
E) Frequency of the D allele does not vary.
Correct Answer:

Verified
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q2: Who proposed that organisms could be organized
Q3: Which of the following scientists argued that
Q4: Which of the following is an example
Q5: A farmer uses triazine herbicide to control
Q6: Explain how one of the following supports
Q7: Parasitic species tend to have simple morphologies.
Q8: Use the following information when answering the
Q9: Evolution by natural selection changes the population
Q10: Fishers typically target the largest, and thus,
Q11: Tourist companies start visiting Island X, where