Multiple Choice
Below gives the data concerning (1) the dependent variable Default which equals 1 if a customer defaults on their loan and 0 if they do not; (2) the independent variable Price of Home, which is the price of the home (in tens) and (3) the independent variable First Purchase which equals 0 if the customer has owned a home before and 1 if this is their first home. Identify and interpret the odds ratio estimate for First Purchase. 
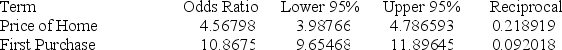
A) Odds ratio: 10.8675; a first-time home buyer is 10 times less likely to default than a buyer who has bought a home before.
B) Odds ratio: 10.8675; a first-time home buyer is 11 times more likely to default than a buyer who has bought a home before.
C) Odds ratio: 10.8675; a first-time home buyer is 10% times more likely to default than a buyer who has bought a home before.
D) Odds ratio: 10.8675; a first-time home buyer is 11% times more likely to default than a buyer who has bought a home before.
Correct Answer:

Verified
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q15: It is not possible to apply a
Q16: Define point estimate. What does the point
Q17: What are the three layers in a
Q18: The odds of an event occurring is:
Q19: Linear discriminate analysis can classify accurately even
Q21: The AIC never penalizes the model for
Q22: Parametric predictive analysis can be used to
Q23: In logistic regression, the difference between a
Q24: What is JMP and how is it
Q25: Which predictive analytic technique would be best