Multiple Choice
Suppose that a bank wishes to predict whether or not an existing holder of its Silver credit card will upgrade, for an annual fee, to its Platinum credit card. To do this, the bank carries out a pilot study that randomly selects 40 of its existing Silver card holders and offers each Silver card holder an upgrade to its Platinum card. Here, the response variable Upgrade equals 1 if the Silver card holder decided to upgrade and 0 otherwise. Moreover, the predictor variable Purchases is last year's purchases (in thousands of dollars) by the Silver card holder, and the predictor variable PlatProfile equals 1 if the Silver card holder conforms to the bank's Platinum profile and 0 otherwise. Below is the classification tree they derived from the data collected in the study. 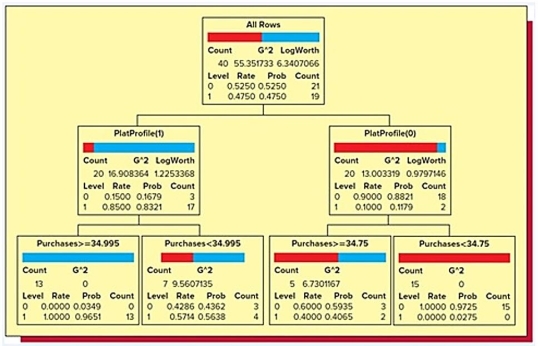 Assume they classify those with an upgrade probability estimate of at least .5 as upgraders. Based on this classification tree, a member of the study sample who made $50,450 in purchases last year, did not conform to the bank's Platinum profile, and upgraded to the Platinum card would be…
Assume they classify those with an upgrade probability estimate of at least .5 as upgraders. Based on this classification tree, a member of the study sample who made $50,450 in purchases last year, did not conform to the bank's Platinum profile, and upgraded to the Platinum card would be…
A) accurately classified as an upgrader.
B) accurately classified as a non-upgrader.
C) inaccurately classified as an upgrader.
D) inaccurately classified as a non-upgrader.
Correct Answer:

Verified
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q39: Dividing the entire data set into a
Q40: A quantitative variable which can have only
Q41: For a sufficiently large value of k,
Q42: An internet service provider (ISP) has randomly
Q43: An internet service provider (ISP) has randomly
Q45: The nearest neighbors to an observation are
Q46: An automobile finance company analyzed a sample
Q47: An automobile finance company analyzed a sample
Q48: An automobile finance company analyzed a sample
Q49: A classification tree is useful for predicting