Multiple Choice
An automobile finance company analyzed a sample of recent automobile loans to try to determine key factors in identifying borrowers who would be likely to default on their auto loan. The response variable Default equals 1 if the borrower defaulted during the term of the loan and 0 otherwise. The predictor variable AutoDebt% was the ratio (expressed as a percent) of the required loan payments to the borrower's take-home income at the time of purchase. JobTime was the number of years the borrower had worked at their current job at the time of purchase. CredScore was the borrower's credit score at the time of purchase. Below is part of the classification tree the finance company derived from the data collected in the study. Assume they classify those with a default probability estimate of at least .5 as Defaulters. 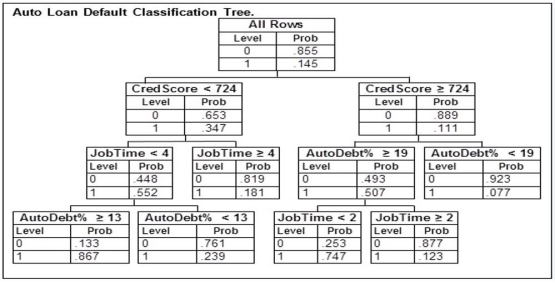 A potential borrower with a credit score of 724 who has been at their current job for 3 years and has a monthly salary of $6,000 would like to apply for a loan. To be approved for the loan they would need to be classified as a non-Defaulter. Of the following monthly payments, which is the highest this loan could have to be approved for this potential borrower?
A potential borrower with a credit score of 724 who has been at their current job for 3 years and has a monthly salary of $6,000 would like to apply for a loan. To be approved for the loan they would need to be classified as a non-Defaulter. Of the following monthly payments, which is the highest this loan could have to be approved for this potential borrower?
A) $591
B) $964
C) $1,295
D) None of these monthly payments would allow them to be classified as a non-Defaulter.
E) There is insufficient information to determine the maximum allowable monthly payment.
Correct Answer:

Verified
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q46: An automobile finance company analyzed a sample
Q47: An automobile finance company analyzed a sample
Q48: An automobile finance company analyzed a sample
Q49: A classification tree is useful for predicting
Q50: The naive Bayes' classification procedure can be
Q52: An automobile finance company analyzed a sample
Q53: The confusion matrix is not a good
Q54: Because different classification techniques will perform better
Q55: An MBA admissions officer wishes to predict
Q56: A cable television company has randomly selected