Essay
An executive has been offered a compensation package that includes stock options. The current stock price is $30/share, and she has been offered a call option on 2000 shares, which can be exercised five years from now at a price of $42/share. Therefore, if the market price of the shares in five years is more than $42/share, she can buy 2000 shares at $42/share, and then immediately sell the shares at the market price, earning a riskless profit. If the market price of the shares was less than $42/share, she will obviously choose not to exercise the option, and would have zero profit.
Assume the price of the stock can be modeled as exponential growth (compounding), which could be calculated as: 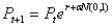 where,
where, 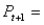 stock price in next period (i.e., price next year)
stock price in next period (i.e., price next year) 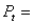 current stock price
current stock price 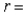 annual growth rate of the stock price, which has been 10%
annual growth rate of the stock price, which has been 10% 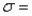 annual volatility, which is estimated to be 18%
annual volatility, which is estimated to be 18% 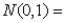 normal random variable with mean of zero and standard deviation of 1
normal random variable with mean of zero and standard deviation of 1
-Simulate the price of the stock in five years by calculating five annual increments (steps) with this model, starting from the current price of $30/share. For each price simulated five years from now, model the exercise decision and calculate the resulting profit, which should then be discounted for five years at the current discount rate (5%) to obtain the present value of the options. What is the expected value of the stock options?
Correct Answer:

Verified
The mean discounted ...View Answer
Unlock this answer now
Get Access to more Verified Answers free of charge
Correct Answer:
Verified
View Answer
Unlock this answer now
Get Access to more Verified Answers free of charge
Q8: Perform a simulation assuming the plant will
Q9: Which @RISK function can be used to
Q11: Assume that one of the bidders bids
Q12: A key objective in cash flow models
Q14: (A) Assuming we are risk neutral, use
Q16: You would like to develop a simulation
Q17: Estimate the mean and standard deviation of
Q18: Which of the following is typically not
Q20: The @RISK function RISKUNIFORM (0,1)is essentially equivalent
Q27: What is the probability that your portfolio's