Multiple Choice
Every year on Groundhog Day (February 2) , the famous groundhog Punxsutawney Phil tries to predict whether there will be 6 more weeks of winter.
Suppose that you plan to take a random sample of 23 years and use weather data to determine the proportion of these years the groundhog's prediction was correct.
If the groundhog has a 50-50 chance of making a correct prediction, the spread of the sampling distribution of 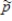 for samples of size 23 is:
for samples of size 23 is:
A) 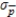 = 0.1474
= 0.1474
B) 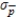 = 0.1043
= 0.1043
C) 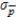 = 0.2085
= 0.2085
D) 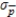 = 0.0435
= 0.0435
E) 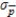 = 0.0870
= 0.0870
Correct Answer:

Verified
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q3: For tests of hypotheses about μ, β
Q4: The level of significance of a test
Q8: Explain in your own words the distinction
Q17: When performing tests of hypotheses, there are
Q21: One criticism of reading comprehension tests is
Q23: Which of the following specify legitimate pairs
Q25: Assuming a random sample from a large
Q27: As children grow they develop what is
Q29: Researchers conducted a survey of 326 dog
Q34: The power of a test is the