Essay
The neoclassical growth model predicts that for identical savings rates and population growth rates, countries should converge to the per capita income level. This is referred to as the convergence hypothesis. One way to test for the presence of convergence is to compare the growth rates over time to the initial starting level, i.e., to run the regression , where is the average annual growth rate of GDP per worker for the 1960-1990 sample period, and is GDP per worker relative to the United States in 1960. Under the null hypothesis of no convergence, , implying ("beta") convergence. Using a standard regression package, you get the following output: Dependent Variable: G6090
Method: Least Squares
Date: 07/11/06 Time: 05:46
Sample: 1104
Included observations: 104
White Heteroskedasticity-Consistent Standard Errors & Covariance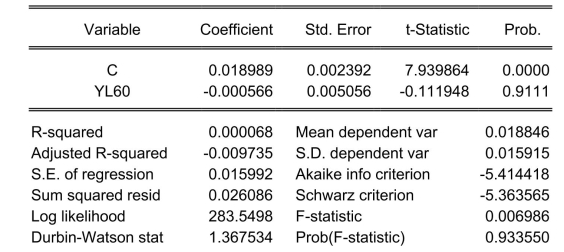
You are delighted to see that this program has already calculated p-values for you.
However, a peer of yours points out that the correct p-value should be 0.4562.
Who is right?
Correct Answer:

Verified
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q22: Consider the sample regression function
Q23: Imagine that you were told that
Q24: Assume that your population regression function
Q25: (continuation from Chapter 4) Sir Francis
Q26: (Requires Appedix material and Calculus) Equation
Q29: Your textbook discussed the regression model
Q30: (continuation from Chapter 4, number 3)You
Q31: The only difference between a one- and
Q31: The proof that OLS is BLUE
Q32: In general, the t-statistic has the