Multiple Choice
Table 5.3
King Supply makes four different types of plumbing fixtures: W, X, Y and Z. The contribution margins for these products are: $70 for Product W, $60 for Product X, $90 for Product Y and $100 for Product Z. Fixed overhead is estimated at $5,500 per week. The manufacture of each fixture requires four machines, Machines #1, 2, 3 and 4. Each of the machines is available for 40 hours a week and there is no setup time required when shifting from the production of one product to any other. The processing requirements to make one unit of each product are shown in the table. Weekly product demand for the next planning period has been forecasted as follows: 70 Ws, 60 Xs, 50 Ys and 30 Zs.
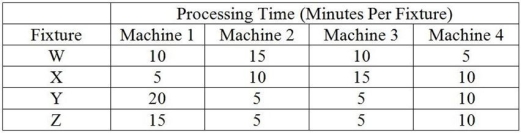
In the questions that follow, the traditional method refers to maximizing the contribution margin per unit for each product, and the bottleneck method refers to maximizing the contribution margin per minute at the bottleneck for each product.
-Use the information in Table 5.3. Using the traditional method, what is the optimal product mix?
A) 70 W, 60 X, 90 Y, 100 Z
B) 70 W, 50 X, 50 Y, 30 Z
C) 70 W, 60 X, 47 Y, 30 Z
D) 70 W, 47 X, 50 Y, 30 Z
Correct Answer:

Verified
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q67: Managers should produce products with the highest
Q68: The key to preserving bottleneck capacity is
Q69: Table 5.3<br>King Supply makes four different types
Q70: The most controversial aspect of line-flow layout
Q71: Table 5.1<br>A company makes four products that
Q73: Use the process flow diagram to determine
Q74: Figure 5.1<br> <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB1252/.jpg" alt="Figure 5.1
Q75: What is a Drum-Buffer-Rope system for planning
Q76: Given the following data about an assembly
Q77: The process with the least capacity is