Short Answer
A patient with persisting larger-than-normal lymph nodes is suspected to have a T cell lymphoma, a cancer of T lymphocytes. Abnormally enlarged lymph nodes are also found in local infections, when lymphocytes are activated to proliferate there. In order to distinguish between cancer and infection, you take tissue samples from the patient, as well as from a healthy individual, and perform a so-called clonality test. You extract DNA from the tissues and amplify a small chromosomal region that includes the T-cell-receptor ? chain D-J junctions. Amplification is done by PCR, using primers that hybridize to specific DNA sequences flanking the junctions. You then analyze the size distributions of the PCR products by capillary electrophoresis, which makes it possible to distinguish between DNA molecules with small differences in size. Based on the results, presented in the following schematic graphs, you conclude that, unfortunately, it is likely that the patient has developed a T cell lymphoma. Which graph (1 or 2) represents the patient's test results? Write down 1 or 2 as your answer.
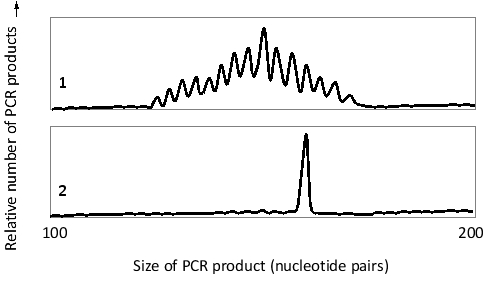
Correct Answer:

Verified
V(D)J recombination in T lymphocytes cr...View Answer
Unlock this answer now
Get Access to more Verified Answers free of charge
Correct Answer:
Verified
View Answer
Unlock this answer now
Get Access to more Verified Answers free of charge
Q23: Blood-group compatibility is an important consideration in
Q24: In the following schematic diagram, which curve
Q25: Indicate whether each of the following descriptions
Q26: Indicate whether each of the following descriptions
Q27: How are natural killer (NK) cells different
Q29: Indicate whether each of the following normally
Q30: Consider two solution chambers of equal volume
Q31: Indicate whether each of the following descriptions
Q32: In antigen presentation to helper T cells
Q33: Indicate whether each of the following descriptions