Multiple Choice
When DMSO dissolves potassium chloride (K+ Cl−) , what is the solvation of the salt due to?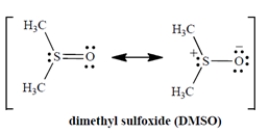
A) The charge-dipole interaction of the sulfur with the K+.
B) The charge-dipole interaction of the oxygen with the K+.
C) The charge-dipole interaction of the oxygen with the Cl−.
D) The hydrogen-bonding interaction of the chloride ion with the C-H bonds.
Correct Answer:

Verified
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q7: Dissolving hexane in water has<br>A) a large
Q8: Draw the structure of 3-hexyn-2-ol.
Q9: Name the compound. Include the appropriate stereochemical
Q10: Consider the equilibria in CCl<sub>4</sub>, an apolar,
Q11: Draw all the alcohols having a molecular
Q13: Drugs are often conjugated to glucuronic acid
Q14: Name the compound with an IUPAC systematic
Q15: Arrange these compounds in order of increasing
Q16: Draw the structure of 3-ethoxy-2-butanethiol (alternate name
Q17: Which compound would form the strongest complex