Multiple Choice
Figure 14.3
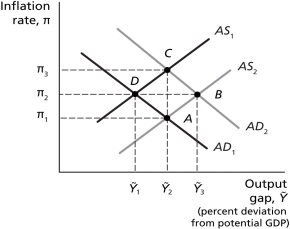
-Refer to Figure 14.3.Suppose the economy is initially at long-run equilibrium and the Bank of Canada increases the target inflation rate,and to hit this rate,it must reduce the real interest rate.The economy then reaches a new,short-run equilibrium point.Assuming expectations are adaptive,the next movement will result in real GDP
A) decreasing back to potential GDP.
B) increasing beyond potential GDP.
C) increasing back to potential GDP.
D) declining below potential GDP.
Correct Answer:

Verified
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q34: For each of the following scenarios,state the
Q35: There is no trade-off between inflation and
Q36: When the economy responds to a supply
Q37: Figure 14.3<br> <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4177/.jpg" alt="Figure 14.3
Q38: Suppose the economy is initially in equilibrium
Q40: Figure 14.3<br> <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4177/.jpg" alt="Figure 14.3
Q41: Use a graph to show the differences
Q42: The economy is in long-run equilibrium when
Q43: Figure 14.1<br> <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4177/.jpg" alt="Figure 14.1
Q44: Assume that the Bank of Canada has