True/False
The singular Sturm-Liouville boundary value problem consisting of the differential equation 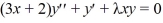 with boundary conditions that both y and
with boundary conditions that both y and 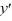 remain bounded as x approaches 0 from the right and that y(1) +
remain bounded as x approaches 0 from the right and that y(1) + 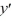 (1) = 0 is self-adjoint.
(1) = 0 is self-adjoint.
Correct Answer:

Verified
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q9: Consider the eigenfunction problem<br> <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TBW1042/.jpg" alt="Consider
Q10: Consider the boundary value problem<br><img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TBW1042/.jpg"
Q11: Consider the eigenfunction problem<br> <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TBW1042/.jpg" alt="Consider
Q12: Consider the Sturm-Liouville problem<br> <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TBW1042/.jpg" alt="Consider
Q13: Consider the boundary value problem<br> <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TBW1042/.jpg"
Q14: Consider the boundary value problem<br><img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TBW1042/.jpg" alt="Consider
Q15: Consider the boundary value problem<br><img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TBW1042/.jpg" alt="Consider
Q16: Consider the boundary value problem<br> <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TBW1042/.jpg"
Q18: Consider the boundary value problem
Q19: Consider the boundary value problem<br> <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TBW1042/.jpg"