Multiple Choice
An antibiotic is being administered intravenously to a patient. Fluid containing 6.5 mg/ of the antibiotic enters the patient's bloodstream at a rate of 100 /hour. The antibiotic is absorbed by the body or otherwise leaves the bloodstream at a rate proportional to the amount present, with a rate constant of 0.4 per hour. Assume the antibiotic is always uniformly distributed throughout the bloodstream.Which of these is a differential equation for the amount of antibiotic, A(t) , in the bloodstream at any time t?
A) 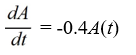
B) 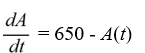
C) 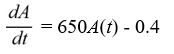
D) 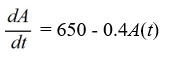
Correct Answer:

Verified
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q1: A portion of the direction field
Q2: Newton's Law of Cooling states that the
Q3: A model for the vertical flight of
Q4: For what values of r is y(t)
Q6: Which of the following are solutions to
Q7: Consider the differential equation x = <img
Q8: Which of the following are solutions to
Q9: Eight differential equations and four slope fields
Q10: Which of the following pairs of values
Q11: A model for the vertical flight of