Multiple Choice
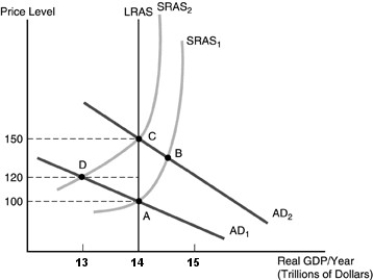
-Refer to the above figure. Suppose the economy is in long-run equilibrium at point A, and the government initiates an expansionary monetary policy to increase aggregate demand. Which of the following is a true statement concerning the differences between what happens when the governmental action is unanticipated and when it is anticipated?
A) The new long-run equilibrium when the increase in aggregate demand is unanticipated is point B while the new long-run equilibrium when the increase in aggregate demand is anticipated is point C.
B) The new long-run equilibrium when the increase in aggregate demand is unanticipated is point B while the new long-run equilibrium when the increase in aggregate demand is anticipated is point A.
C) The new long-run equilibrium will be point C in either case. When the increase in aggregate demand is unanticipated, the economy moves to B in the short run, but when the increase in aggregate demand is anticipated, short-run aggregate supply shifts when the aggregate demand curve shifts, and the economy moves immediately to point C.
D) The new long-run equilibrium is point C in either case. When the increase in aggregate demand is unanticipated, the new short-run equilibrium is point B, but when the increase in aggregate demand is anticipated the new short-run equilibrium is point D.
Correct Answer:

Verified
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q18: The natural rate of unemployment is<br>A) the
Q48: Which of the following would NOT cause
Q67: When the actual unemployment rate is greater
Q84: The stickiness of wages and prices will
Q113: <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB5013/.jpg" alt=" -Refer to the
Q124: The costs associated with changing prices are
Q125: <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB5018/.jpg" alt=" -Use the above
Q140: There is greater support for active policymaking
Q188: According to the policy irrelevance proposition, monetary
Q221: Which of the following statements is consistent