Short Answer
Consider the reaction CO(g)+ 2H2(g) 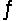 CH3OH(l)at 25°C.
CH3OH(l)at 25°C.
G°f (CO)= -137.3 kJ/mol
G°f (CH3OH)= -166.3 kJ/mol
H°f (CO)= -110.5 kJ/mol
H°f (CH3OH)= -238.7 kJ/mol
S°(CO)= 197.9 J/K·mol
S°(CH3OH)= 126.8 J/K·mol
Calculate value of the equilibrium constant (Kp)for this reaction at 25°C.
Correct Answer:

Verified
1.21  10
10View Answer
Unlock this answer now
Get Access to more Verified Answers free of charge
Correct Answer:
Verified
View Answer
Unlock this answer now
Get Access to more Verified Answers free of charge
Q11: Assuming <span class="ql-formula" data-value="\Delta"><span class="katex"><span
Q17: For the reaction 2C(graphite)+ H<sub>2</sub>(g) <span
Q67: For the reaction H<sub>2</sub>(g)+ S(s) <span
Q82: Which one of the following reactions
Q83: Calculate the equilibrium constant for the
Q84: Which of these species has the highest
Q84: How does the entropy change when a
Q89: At 1500°C the equilibrium constant for
Q92: In the gas phase, formic acid
Q103: The following reaction is spontaneous under