Essay
A model that attracted quite a bit of interest in macroeconomics in the 1970s was the St. Louis model. The underlying idea was to calculate fiscal and monetary impact and long run cumulative dynamic multipliers, by relating output (growth)to government expenditure (growth)and money supply (growth). The assumption was that both government expenditures and the money supply were exogenous. Estimation of a St. Louis type model using quarterly data from 1960:I-1995:IV results in the following output (HAC standard errors in parenthesis): 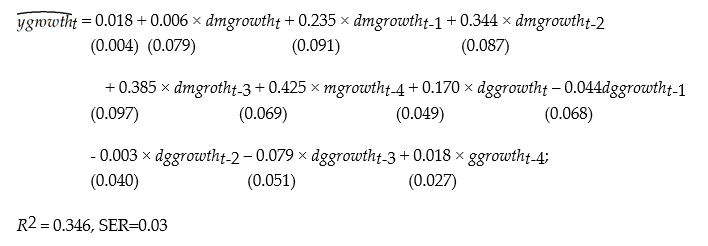
where ygrowth is quarterly growth of real GDP, mgrowth is quarterly growth of real money supply (M2), and ggrowth is quarterly growth of real government expenditures. "d" in front of ggrowth and mgrowth indicates a change in the variable.
(a)Assuming that money and government expenditures are exogenous, what do the coefficients represent? Calculate the h-period cumulative dynamic multipliers from these. How can you test for the statistical significance of the cumulative dynamic multipliers and the long-run cumulative dynamic multiplier?
(b)Sketch the estimated dynamic and cumulative dynamic fiscal and monetary multipliers.
(c)For these coefficients to represent dynamic multipliers, the money supply and government expenditures must be exogenous variables. Explain why this is unlikely to be the case. As a result, what importance should you attach to the above results?
Correct Answer:

Verified
(a)In that case the coefficients represe...View Answer
Unlock this answer now
Get Access to more Verified Answers free of charge
Correct Answer:
Verified
View Answer
Unlock this answer now
Get Access to more Verified Answers free of charge
Q10: Sensitivity analysis of the results may include
Q11: To estimate dynamic causal effects, your textbook
Q12: A seasonal binary (or indicator or dummy)variable,
Q13: The long-run cumulative dynamic multiplier<br>A)cannot be calculated
Q14: (Requires Appendix material)Your textbook states that in
Q16: In time series data, it is useful
Q17: Autocorrelation of the error terms<br>A)makes it impossible
Q18: You are hired to forecast the unemployment
Q19: Given the relationship between the two variables,
Q20: Your textbook estimates the initial relationship