Multiple Choice
The diagram below shows a simplified version of the biochemical pathway responsible for fruit color in peppers.Assume that Enzyme 1 is encoded by gene A (a is a null allele) ,Enzyme 2 is encoded by gene B (b is a null allele) ,and Enzyme 3,which breaks down the chlorophyll present in the fruit,is encoded by gene C (c is a null allele) .In the absence of Enzyme 3,the fruit takes a brown color in the presence of red pigment,but it remains green in the absence of red pigment. 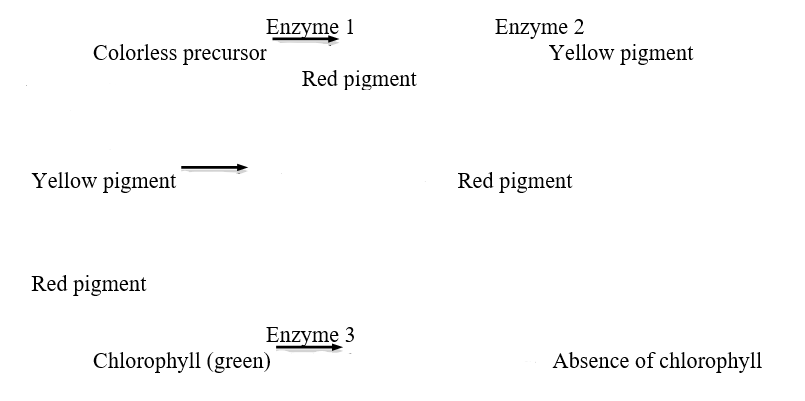
Absence of chlorophyll
a) Consider two genotypically different pure lines that make colorless peppers.If these two plants are crossed,what phenotypes should be observed in the F1?
A) colorless only
B) colorless and yellow only
C) red and yellow only
D) red only
E) yellow only
Correct Answer:

Verified
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q2: In Drosophila,the recessive alleles for brown and
Q3: In Drosophila,two genes affecting body color
Q4: Suppose that pigmentation in rabbits is
Q5: Two new mutant lines of a
Q6: The following example of gene regulation involves
Q7: Loppins can be purple or white,and this
Q8: In swine,when a pure-breeding red is crossed
Q9: Snapdragons with red,normally shaped flowers are
Q10: Two new pure-breeding strains of mouse (strain
Q11: Neurospora is a haploid,filamentous fungus normally having