Essay
Match the term to its definition by filling in the letter or letters before the term in the appropriate blank.
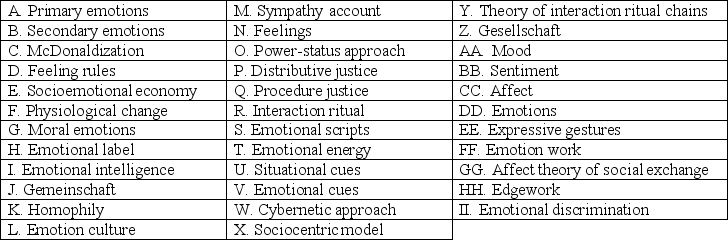 ____ A heightened sense of excitement produced by a feeling of belonging in society.
____ A heightened sense of excitement produced by a feeling of belonging in society.
____ Exchange-based theory in which exchange relationships are thought to produce emotions which are used as an internal source of rewards and punishments for developing cohesion among individuals and groups.
____ Thrill seeking behaviors designed to produce intense emotions.
____ Attributing secondary (i.e. ,human)emotions to our in-groups and not our out-groups.
____ The process of hyperrationality of the service workforce,applying assembly-line techniques to interpersonal work.
____ A diffuse emotional state that lasts a relatively long period of time.
____ Element of emotion referring to the changes in our body that reflect the emotion in a given situation.
____ Element of emotion referring to the terms we use to label our feelings.
____ Expectations about when and how to act excited or angry or any other emotion.
____ Feelings that incorporate situational cues,physiological changes,expressive gestures,and an emotion label.
____ Our ability to control and employ emotions in our social environments.
____ An evaluative component of an emotion.
____ The study of emotion that assumes that social conditions shape our emotions and,in turn,that our emotions act to maintain social structures.
____ In exchange theory,it is the beliefs about the fairness of what people get.
____ A society's expectation about how to experience different emotions.
____ The generation of prescribed emotion in order to meet the demands of a job.
____ Information about when and what emotions are appropriate in a given social setting.
____ Societies in which relationships are based on family and kinship.
____ Element of an emotion referring to the indications we give of the emotion we are experiencing.
____ Rules that tell us how we should feel in different social interactions.
____ Internal states associated with a particular emotion.
____ Societies in which relationships are based on self-interest.
____ The exchange of symbols and emotion between individuals essential to maintaining society.
____ The study of emotions based on the idea that human emotions result from real,anticipated,imagined,or recollected outcomes of social relations.
____ The tendency to be attracted to others who have similar characteristics,such as being from the same ethnic,religious,or social class background.
____ Physiologically grounded emotions that we inherit through evolutionary processes,including anger,fear,depression,and satisfaction.
____ In exchange theory,it is the beliefs about the fairness of the methods used to make distributions.
____ Emotions that derive from primary emotions when we attach varying meanings to primary emotions.
____ A system for regulating emotional resources among people.
____ The amount of sympathy that a person can expect from other people.
____ Theory that emphasizes the role of emotions in maintaining macrosociological institutions.
____ Those emotions that compel us to follow the rules of society.
____ A feeling that has been given meaning by society.
____ Element of emotion that tells when and what emotion is appropriate in a given social interaction.
____ Theory that argues that the primary means of learning about emotions comes from social instruction,primarily through family,friends,and schooling.
Correct Answer:

Verified
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q2: Read the vignette and answer the questions
Q3: Zurcher's concept of emotional scripts most closely
Q4: Your friend Chloe goes through a bad
Q5: Which of the following emotions is considered
Q6: Based on Lofland's analysis of the role
Q7: _is one of the four pillars of
Q8: What did Swidler's research on love in
Q9: What emotion did wheelchair users employ when
Q10: Based on Thoit's treatment of emotions,which of
Q11: Which of the following emotions is an