Multiple Choice
Use the given value of k to complete the table for the inverse variation model . Plot the points on a rectangular coordinate system.
A) 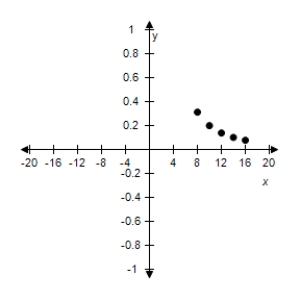
B)
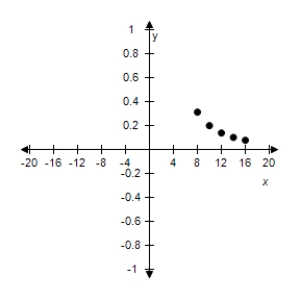
C)
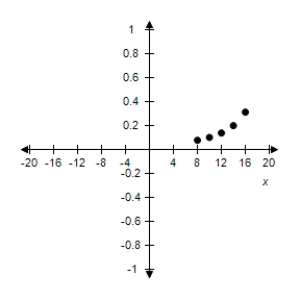
D)
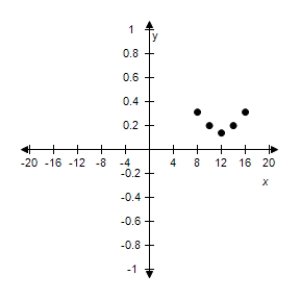
E)
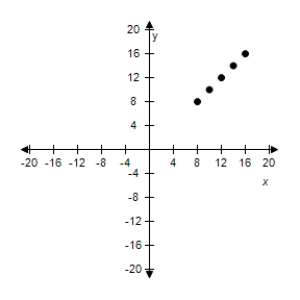
Correct Answer:

Verified
Correct Answer:
Verified
Related Questions
Q38: Property tax is based on the
Q39: A force of 270 newtons stretches a
Q40: Determine whether the variation model is
Q41: Find a mathematical model representing the
Q42: Find a mathematical model representing the
Q44: Use the given value of k
Q45: The frequency of vibrations of a piano
Q46: An oceanographer took readings of the
Q47: Use the fact that the resistance of
Q48: Assume that y is directly proportional