Multiple Choice
Following an acute virus infection in which the host clears the virus by approximately one week post-infection, a population of virus-specific memory CD8 T cells is maintained and can be detected for months to years post-infection. In mice with a knockout of a single cytokine, virus-specific memory CD8 T cells cannot be maintained, and disappear over time as shown in Figure. 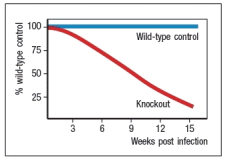
The most likely identity of the cytokine that is missing in these knockout mice is:
A) IL-15
B) IL-2
C) IL-21
D) IL-23
E) IL-4
Correct Answer:

Verified
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q18: It is well documented that antibody affinities
Q19: In response to an intracellular bacterial
Q20: Vaccinia virus, used to immunize individuals against
Q21: Studies in mice have shown that
Q22: Allergic airway inflammation can be induced in
Q24: The immune response to helminthic worm infections
Q25: Initially after an infection, the majority of
Q26: Salmonella typhimurium is a Gram-negative bacterial
Q27: A set of mice are each immunized
Q28: Toxoplasma gondii is a single-celled parasitic