Multiple Choice
Allergic airway inflammation can be induced in mice by immunizing them with an allergen that produces a TH2 effector response, and then challenging the immunized mice with an inhaled form of that allergen. In this disease model, the TH2 effector cells present in the lung respond to the inhaled allergen challenge by producing type 2 cytokines that recruit eosinophils and induce airway inflammation. In addition, a component of this TH2 response is antigen-independent, as shown by the effects of administering a neutralizing antibody along with the allergen challenge. This neutralizing antibody (anti-'X' IgG) has the effects shown in Figure Q14) . 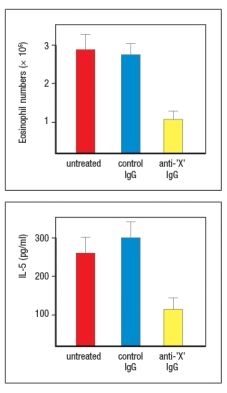 antibody was shown to inhibit the response of the TH2 cells, and therefore is likely to be:
antibody was shown to inhibit the response of the TH2 cells, and therefore is likely to be:
A) A neutralizing antibody to IL-12
B) A neutralizing antibody to IL-4
C) A neutralizing antibody to TSLP
D) A neutralizing antibody to STAT4
E) A neutralizing antibody to IL-13
Correct Answer:

Verified
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q17: Inflammatory bowel disease (colitis) is a
Q18: It is well documented that antibody affinities
Q19: In response to an intracellular bacterial
Q20: Vaccinia virus, used to immunize individuals against
Q21: Studies in mice have shown that
Q23: Following an acute virus infection in which
Q24: The immune response to helminthic worm infections
Q25: Initially after an infection, the majority of
Q26: Salmonella typhimurium is a Gram-negative bacterial
Q27: A set of mice are each immunized