Essay
An infant is admitted to the hospital with a history of recurrent and persistent bacterial infections. His physician suspects he has an immunodeficiency disease, and obtains a sample of the patient's peripheral blood. The white blood cells are analyzed by antibody staining followed by flow cytometry, and the results are shown in Figure. 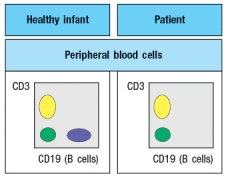
To determine the origin of the peripheral blood cell defect, a bone marrow biopsy is taken from the patient and compared to a healthy control, as shown in Figure.
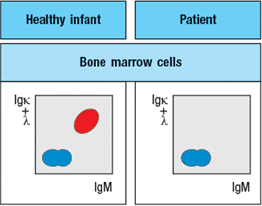
To obtain additional information, bone marrow cells are treated with a chemical that permeabilizes the cell membrane, allowing antibodies to enter the cells and bind to their target antigens within the cells, a technique known as ‘intracellular staining’. The results of this analysis are shown in Figure .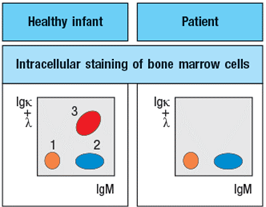
a) What are populations 1, 2, and 3 in Figure?
b) In the analysis of cell surface expression (non-permeabilized bone marrow cells), what are the IgMlo Igκ+λneg cells as indicated by the arrow in Figure? 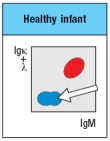
c) What is the most likely defect causing the patient's immunodeficiency?
The results shown above indicate a specific defect in B cell development. To help identify the defective or missing protein in the patient's developing B cells, bone marrow cells are isolated and protein lysates are prepared for immunoblotting. A series of antibodies are tested and the results are shown in Figure.
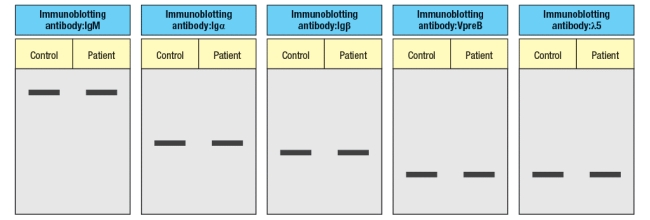
d) Given the results from the immunoblotting experiments, what is the most likely candidate molecule (or type of molecule) responsible for the patient's immunodeficiency disease?
Correct Answer:

Verified
a) Population 1 is pro-B cells that have...View Answer
Unlock this answer now
Get Access to more Verified Answers free of charge
Correct Answer:
Verified
View Answer
Unlock this answer now
Get Access to more Verified Answers free of charge
Q19: The final stages of T cell
Q20: B-1 B cells are considered a component
Q21: T cell development in the thymus shares
Q22: In different mammalian species, the ratio
Q23: B cell development in the bone marrow
Q25: While many cell types in the thymus
Q26: One feature of <span class="ql-formula"
Q27: A wild-type mouse that is heterozygous for
Q28: A key step in the development of
Q29: The mouse thymus normally contains about