Multiple Choice
Streptococcus pneumoniae is a Gram-positive bacterium that colonizes the mucosal surface of the upper respiratory tract in humans. The presence of this bacterium in the nose and throat is widespread in the population, and in most people, colonization with Strep. pneumoniae is asymptomatic. Figure shows a comparison of in vitro growth curves of the wild-type strain of Strep. pneumoniae, as well as a Strep. pneumoniae mutant strain with a defect in one bacterial gene. The graph on the right shows the growth curve following addition of lysozyme during the logarithmic phase of bacterial growth. 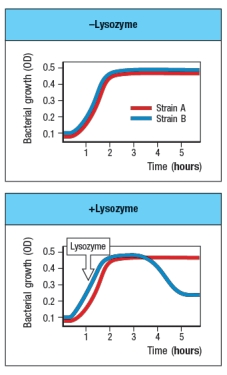
Which statement could account for the data in these graphs?
A) Strain B is wild-type Strep. pneumoniae, and strain A is a mutant that cannot modify its peptidoglycan to be lysozyme-resistant.
B) Strain B is wild-type Strep. pneumoniae, and strain A is a mutant that that expresses increased levels of LPS.
C) Strain A is wild-type Strep. pneumoniae, and strain B is a mutant that cannot modify its peptidoglycan to be lysozyme-resistant.
D) Strain A is wild-type Strep. pneumoniae, and strain B is a mutant that secretes an enzyme that inactivates lysozyme.
E) Strain A is wild-type Strep. pneumoniae, and strain B is a mutant that cannot grow well in vitro.
Correct Answer:

Verified
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q2: Epithelial surfaces provide the first line of
Q3: The C3 convertase of the alternative complement
Q4: Neutrophils regulate the production of active cathelicidins
Q5: Opsonization of pathogens by both antibodies and
Q6: The importance of complement activation as an
Q8: Mannose binding lectins (MBL) and ficolins are
Q9: Although the complement cascade can be initiated
Q10: The C3 convertase amplifies the process of
Q11: Although homozygous deficiencies in complement regulatory proteins
Q12: B cells express a complement receptor that