Multiple Choice
Electrocardiographs (ECGs or EKGs) provide data about the electrical activity of the heart. By placing a series of "leads" on a person's chest, the electrical activity of the heart can be recorded and analyzed in order to detect irregular heartbeats (arrhythmias) and other conditions. The figure below shows a normal EKG tracing for one cardiac cycle.
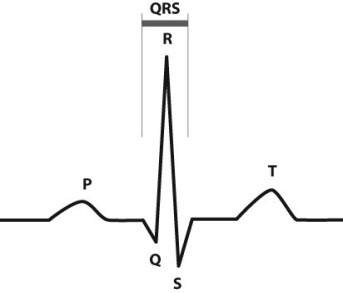 The P region represents electrical activity spreading through the atria. The QRS region represents electrical activity spreading through the ventricles. The T region represents electrical activity in the ventricles returning to rest.
The P region represents electrical activity spreading through the atria. The QRS region represents electrical activity spreading through the ventricles. The T region represents electrical activity in the ventricles returning to rest.
-Suppose a person's AV node in their heart suddenly stopped sending signals to the rest of the heart. How would this person's EKG differ from normal?
A) The EKG would have a taller P region.
B) The EKG would not have a QRS region.
C) The EKG would have a shorter T region.
D) The EKG would not have a gap between the S and T regions.
Correct Answer:

Verified
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q39: Excessive accumulation of fluid in tissues outside
Q40: How long do human red blood cells
Q41: Arteries are distinguished from veins based on
Q42: In which of the following human blood
Q43: Myocardial infarction, also called a heart attack,<br>A)
Q45: Electrocardiographs (ECGs or EKGs) provide data about
Q46: Using a stethoscope, you listen to a
Q47: Which of the following animals has a
Q48: One way that substances move between blood
Q49: In mammals, blood returning from the head