Multiple Choice
What is the standard cell potential for a voltaic cell using the Pb2/Pb and Mg2/Mg half-reactions? Which metal is the cathode? Standard Reduction
Potentials (volts) in Aqueous Solution 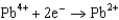 1.80
1.80 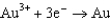 1.50
1.50 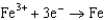 0.771
0.771 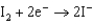 0.535
0.535 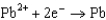 0.124
0.124 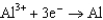 1.66
1.66 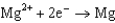 2.37
2.37 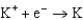 2.93
2.93
A) (2.25 V, Pb is the cathode)
B) (2.25 V, Mg is the cathode)
C) (2.25 V, Mg is the cathode)
D) (2.25 V, Pb is the cathode)
E) (2.49 V, Mg is the cathode)
Correct Answer:

Verified
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q49: The capacity of a battery usually is
Q50: When aluminum metal is obtained from aluminum
Q51: Oxidation is the _<br>A)gain of electrons.<br>B)loss of
Q52: The following reaction is called the "super
Q53: Where in the periodic table do you
Q55: What is the most important use for
Q56: What constitutes a standard hydrogen electrode?
Q57: Which statement about a cathode in a
Q58: The charge supplied by a battery can
Q59: If the potential of a voltaic cell