Multiple Choice
The values of 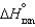 and
and 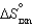 are shown for the following equilibrium reaction. What makes the equilibrium constant larger at low temperature?
are shown for the following equilibrium reaction. What makes the equilibrium constant larger at low temperature? 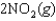
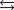
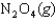 H 58.02 kJ/mol, S 176.5 J/mol K
H 58.02 kJ/mol, S 176.5 J/mol K
A) The negative value of H is dominant at all temperatures.
B) The negative value of S is dominant at all temperatures.
C) The negative value of S is combined with the small value of T.
D) The negative value of H is combined with the small value of T.
Correct Answer:

Verified
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q61: Which of the following is the best
Q62: According to the second law of thermodynamics,
Q63: Perfect crystals of carbon monoxide (CO) are
Q64: Which, if any, of statements A-D is
Q65: If for a given chemical reaction at
Q67: Which statement is true of the ideal
Q68: Given the following data, determine the molar
Q69: Suppose <font face="symbol"></font>G<font face="symbol"></font> is 25.0 kJ/mol
Q70: If K for a reaction is large,
Q71: Hydrochloric acid (HCl) reacts with sodium hydroxide