Multiple Choice
Which of the presented mechanisms would be the most energetically favorable and thus the most likely mechanism to actually occur for the following free radical chain reaction?
(bond dissociation energies - H-H = 104 kcal/mol; Cl-Cl = 58 kcal/mol; H-Cl = 103 kcal/mol)
H2 + Cl2 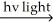 2 HCl
2 HCl
A) H2 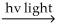 H∙ + H∙
H∙ + H∙
H∙ + Cl2 → Cl∙ + HCl
H∙ + Cl∙ → HCl
B) Cl2 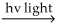 Cl∙ + Cl∙
Cl∙ + Cl∙
Cl∙ + H2 → H∙ + HCl
H∙ + Cl2 → HCl + Cl∙
C) H2 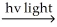 H∙ + H∙
H∙ + H∙
H∙ + Cl2 → Cl∙ + HCl
Cl∙ + H2 → HCl + H∙
D) Cl2 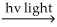 Cl∙ + Cl∙
Cl∙ + Cl∙
Cl∙ + H2 → H∙ + HCl
H∙ + Cl∙ → HCl
Correct Answer:

Verified
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q42: The hydrogen atom abstraction step in the
Q43: The hydrogen atom abstraction step in the
Q44: What reactive intermediate is formed when CHBr<sub>3
Q45: Provide the structure of the transition state
Q46: Given an activation energy of 15 kcal/mol,
Q48: Provide the major organic product that results
Q49: Chlorination of methane can result in a
Q50: In the reaction of Cl<sub>2</sub> with ethane
Q51: If the percentage of the axial onformer
Q52: Consider the conversion of X to Z