Multiple Choice
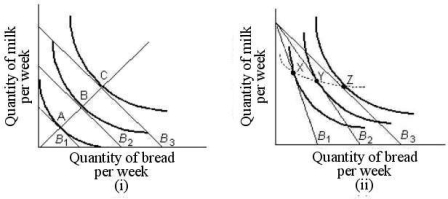 FIGURE 6- 8
FIGURE 6- 8
-Refer to Figure 6- 8. In part (i) , the line joining points A, B, and C is known as , which shows how .
A) a price- consumption line; consumption changes as money income and relative prices change
B) an indifference map; the value of various combinations of two goods changes.
C) an income- consumption line; consumption changes as income changes, with relative prices held constant
D) a price- consumption line; consumption changes as relative prices change, with money income constant
E) an income- consumption line; consumption changes with changing relative prices and constant income
Correct Answer:

Verified
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q1: <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB5438/.jpg" alt=" FIGURE 6- 10
Q2: <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB5438/.jpg" alt=" FIGURE 6- 3
Q4: <span class="ql-formula" data-value="\quad\quad\quad\quad\quad\quad\quad\quad\quad\quad\quad\text { Toffee (bars) }"><span
Q5: Marginal utility theory is about<br>A) proving that
Q7: The marginal rate of substitution measures the
Q8: Suppose a consumer can purchase only two
Q9: An individual's consumer surplus from some product
Q10: The Smith family is allocating its monthly
Q11: Marginal utility analysis predicts a downward- sloping
Q119: The table below shows the quantities of